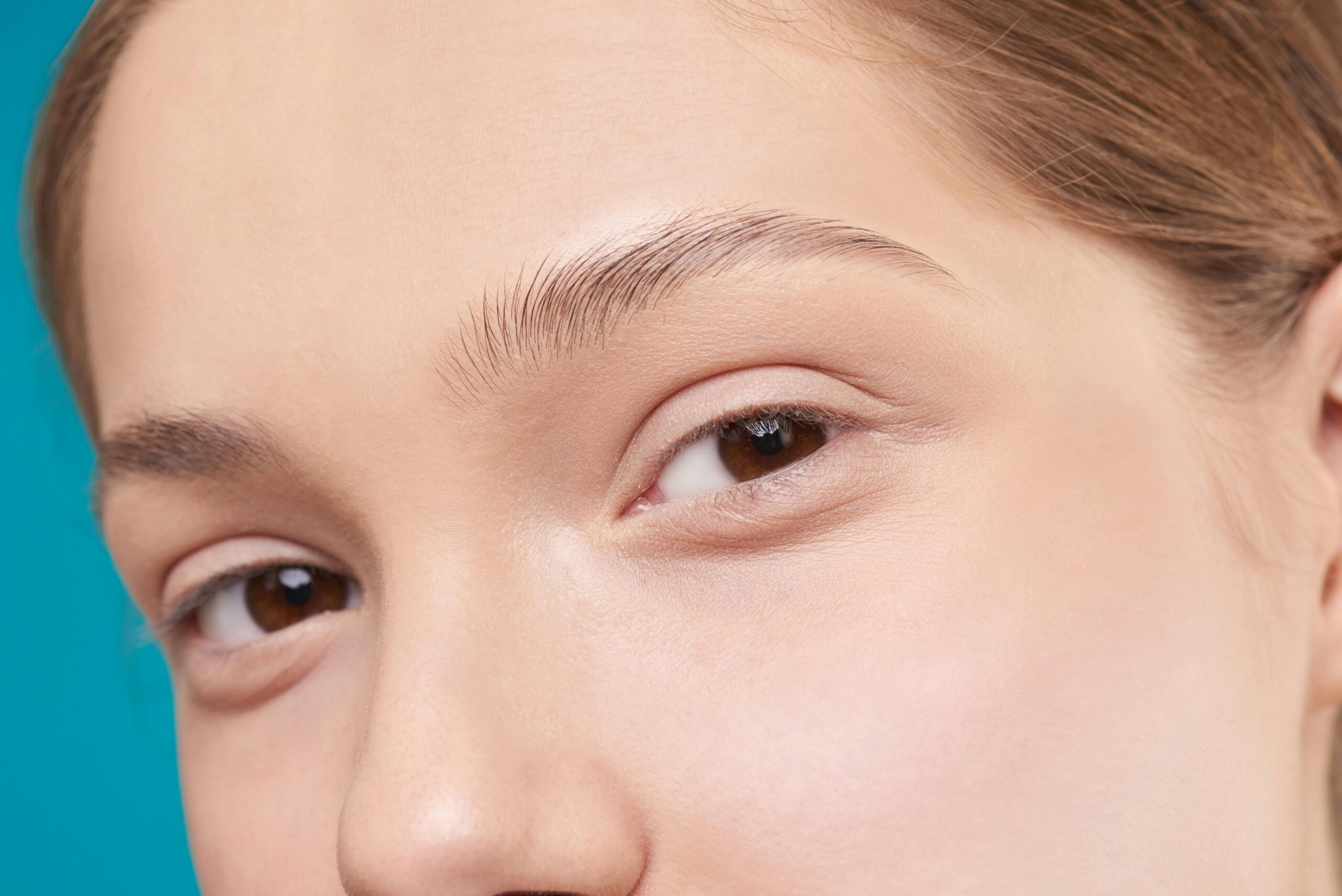
When it comes to skincare, terms like hyperpigmentation and dark spots are often used interchangeably. But did you know they aren’t exactly the same thing? Understanding the difference between these two common skin concerns is key to choosing the right treatments. In this guide, we’ll break down Hyperpigmentation vs Dark Spots, explain what causes them, and provide effective treatment options to help you achieve clearer, more even-toned skin.
Table of Contents
What is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is a broad term used to describe any condition where certain areas of the skin become darker than the surrounding skin. This happens when the skin produces excess melanin, the pigment that gives your skin its color. Hyperpigmentation can appear as large patches, small spots, or even cover large areas of the skin.
Common Causes of Hyperpigmentation:
- Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to UV rays stimulates melanin production, leading to sun spots or age spots (also known as solar lentigines).
- Inflammation: Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) can result from acne, eczema, or other skin injuries. Once the skin heals, dark marks may be left behind.
- Hormonal Changes: Conditions like melasma, often triggered by pregnancy or birth control pills, cause brown or grayish patches on the skin.
- Medications or Medical Conditions: Certain drugs, like chemotherapy medications, and medical conditions, such as Addison’s disease, can cause hyperpigmentation.
What are Dark Spots?
Dark spots (also called age spots, liver spots, or sun spots) are a specific type of hyperpigmentation. They are small, flat, and usually appear on areas of the skin most exposed to the sun, like the face, hands, shoulders, and arms. Dark spots are mainly caused by sun damage and are often associated with aging, though they can also result from acne scars or other skin trauma.
Main Causes of Dark Spots:
- UV Exposure: The leading cause of dark spots is cumulative sun exposure over time, causing the skin to produce excess melanin in targeted areas.
- Acne Scarring: After a pimple heals, it may leave a lingering dark spot called post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
- Hormonal Changes: Similar to hyperpigmentation, hormonal imbalances can trigger dark spots, particularly melasma.
Hyperpigmentation vs Dark Spots: Key Differences
While hyperpigmentation and dark spots share the common factor of increased melanin production, the key difference lies in the scope and causes.
- Scope and Appearance:
- Hyperpigmentation: A broader term for skin darkening, which can appear in large patches or over larger areas of the skin.
- Dark Spots: Specific, small, and isolated spots often caused by sun exposure or acne.
- Causes:
- Hyperpigmentation: Can be caused by a wide range of factors, including hormonal changes, inflammation, and medications.
- Dark Spots: Primarily caused by sun exposure, but can also result from acne or other minor skin damage.
- Treatment Approach:
- While dark spots are a form of hyperpigmentation, treating hyperpigmentation may involve more intensive and long-term strategies due to the variety of causes, whereas dark spots can often be treated with over-the-counter products focused on sun damage or scarring.
How to Treat Hyperpigmentation vs Dark Spots
Understanding the cause and type of pigmentation is crucial to selecting the right treatment. Here’s a look at effective ways to treat both hyperpigmentation and dark spots.
1. Sunscreen: Prevention is Key
No matter what kind of hyperpigmentation or dark spots you’re dealing with, sunscreen is the most important step in your skincare routine. Daily use of a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher can prevent further darkening of existing spots and stop new spots from forming.

Top Pick: EltaMD UV Clear Broad-Spectrum SPF 46 – Lightweight and perfect for sensitive skin, this sunscreen not only protects against UV rays but also contains niacinamide to reduce pigmentation.
2. Vitamin C: Brightening and Antioxidant Protection
Vitamin C is one of the most effective ingredients for treating dark spots and hyperpigmentation. It works by inhibiting melanin production and brightening the skin. Look for a high-quality vitamin C serum to use daily for visible improvement over time.

Top Pick: SkinCeuticals C E Ferulic – This dermatologist-recommended serum is a powerhouse for fading dark spots and protecting against free radicals.
3. Niacinamide: Reduce Inflammation and Brighten
Niacinamide, a form of vitamin B3, works to reduce inflammation and inhibit melanin transfer, making it effective for treating both dark spots and hyperpigmentation caused by acne or sun damage.
Top Pick: The Ordinary Niacinamide 10% + Zinc 1% – A budget-friendly serum that targets pigmentation, redness, and acne scars.
4. Retinoids: Speed Up Cell Turnover
Retinoids are known for increasing skin cell turnover, helping to fade dark spots and hyperpigmentation faster. Prescription-strength retinoids (like tretinoin) are more powerful, but even over-the-counter retinol can be effective.

Top Pick: Differin Gel (Adapalene) – This OTC retinoid gel is great for treating acne and fading the dark spots left behind.
5. Hydroquinone: The Gold Standard for Pigmentation
For more severe cases of hyperpigmentation, hydroquinone is often the gold standard. It works by blocking melanin production and is available in both prescription and over-the-counter formulations. However, it should be used cautiously and under the guidance of a dermatologist.

Top Pick: Ambi Fade Cream with 2% Hydroquinone – A popular and affordable option for treating stubborn dark spots.
6. Exfoliating Acids: Glycolic Acid and Lactic Acid
Exfoliating acids like glycolic acid and lactic acid help to slough away dead skin cells, allowing newer, brighter skin to emerge. Regular use can significantly improve the appearance of dark spots and uneven skin tone.

Top Pick: The Ordinary Glycolic Acid 7% Toning Solution – A gentle exfoliator that helps brighten and even out skin tone over time.
7. Laser Treatments: For Stubborn Cases
For more severe or resistant forms of hyperpigmentation and dark spots, laser treatments can be a highly effective option. These treatments work by targeting melanin in the skin and breaking up the pigment. However, laser treatments should always be performed by a qualified professional and may require multiple sessions.
Preventing Hyperpigmentation and Dark Spots
Prevention is often easier than treatment. Incorporating the following habits into your skincare routine can help keep dark spots and hyperpigmentation at bay:
- Wear Sunscreen Daily: Even on cloudy days or indoors, UV rays can cause skin damage.
- Limit Sun Exposure: Wear protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses, and avoid peak sun hours.
- Use Gentle Products: Avoid harsh scrubbing or picking at the skin, which can worsen hyperpigmentation.
- Be Consistent with Treatments: Skincare treatments for pigmentation take time, so consistency is key.
Conclusion
While hyperpigmentation and dark spots both result from excess melanin production, the underlying causes and treatments can vary. By understanding the difference between Hyperpigmentation vs Dark Spots, you can choose the right skincare routine and products to effectively address your specific skin concerns. With a combination of the right ingredients—like vitamin C, retinoids, and niacinamide—and consistent sun protection, you can fade pigmentation and achieve clearer, more radiant skin over time.






